[COVID-19] Government Responses on the Coronavirus Disease 2019
July 1, 2020
This page is an archive of past feature pages.
Please note that the information contained herein is not updated.
Please note that the information contained herein is not updated.
Latest Information
- Border enforcement measures (Overview) (Ministry of Foreign Affairs) (July 1)
- Confirmed Cases of COVID-19 by Country (the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Website) (July 1)
- 38th Meeting of the Novel Coronavirus Headquarters (PM in Action) (June 18)
- Analysis and Recommendations of the Response to the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) (Summary) (Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare) (May 29)
- Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Summary) (Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare) (May 25)
- Declaration of the Lifting of the State of Emergency (Overview | Guidelines for the Lifting the State of Emergency) (May 25)
- Press Conference by the Prime Minister (Government Internet TV | Opening Statement) (May 25)
- Confirmed Cases of COVID-19 by Country (the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Website) (July 1)
- 38th Meeting of the Novel Coronavirus Headquarters (PM in Action) (June 18)
- Analysis and Recommendations of the Response to the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) (Summary) (Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare) (May 29)
- Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Summary) (Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare) (May 25)
- Declaration of the Lifting of the State of Emergency (Overview | Guidelines for the Lifting the State of Emergency) (May 25)
- Press Conference by the Prime Minister (Government Internet TV | Opening Statement) (May 25)
Government Responses
On May 25, the Declaration of the State of Emergency was lifted nationwide, based on the assessment of the current situation in light of the three criteria: the state of infections, medical treatment structure, and monitoring structure. The government remains vigilant and is undertaking a set of measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 infections and restore socioeconomic activities, based on the Basic Policies for Prevention and Control of the Novel Coronavirus.
Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Revised on May 25) (Summary)
Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Revised on May 21) (Summary)
Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Revised on May 14) (Summary)
Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Revised on May 4) (Summary | Key Points)
Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Revised on April 16) (Summary)
Basic Policies for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Revised on April 7) (Overview | Full Text)
(Emergency Economic Measures)
On April 7, 2020, the Government decided upon the Emegency Economic Measures for Response to COVID-19 to protect the lives and lifestyles of the public and move toward economic recovery (revised on April 20, 2020). On April 30, the first supplementary budget for FY2020 to implement those measures was enacted by the Diet. On June 12, 2020, the second supplemntary budget for FY2020, which aims at enhancing the government's measures to protect the lives and lifestyles of the public from COVID-19 and move forward economic recovery, was also enacted by the Diet.
Emergency Economic Measures (Overview | Full Text)
Second Supplementary Budget (Overview)
First Supplementary Budget (Overview)
Basic Strategy
Three Pillars of Basic Strategy
<Overall Goal>
To maximize efforts to suppress transmission and to minimize socio-economic damage
1. Early detection of and early response to clusters
2. Enhancement of intensive care and securing medical service system for the severely ill patients, including medical equipments (Ventilator, ECMO, etc)
3. Bahavior modification of citizens
Rationale of the Government Responses
In order to end this epidemic as soon as possible, it is extremely important to prevent one cluster from developing another cluster, and the comprehensive measures must be taken. It is also significantly important to curtail the rate of increase in patients as much as possible through these preventative measures, in order to control the epidemic in Japan.
Moreover, this is also the time to establish and improve arrangements including the health system to deliver necessary medical care especially for the severe patients, to prepare for the possible increase of patients in Japan.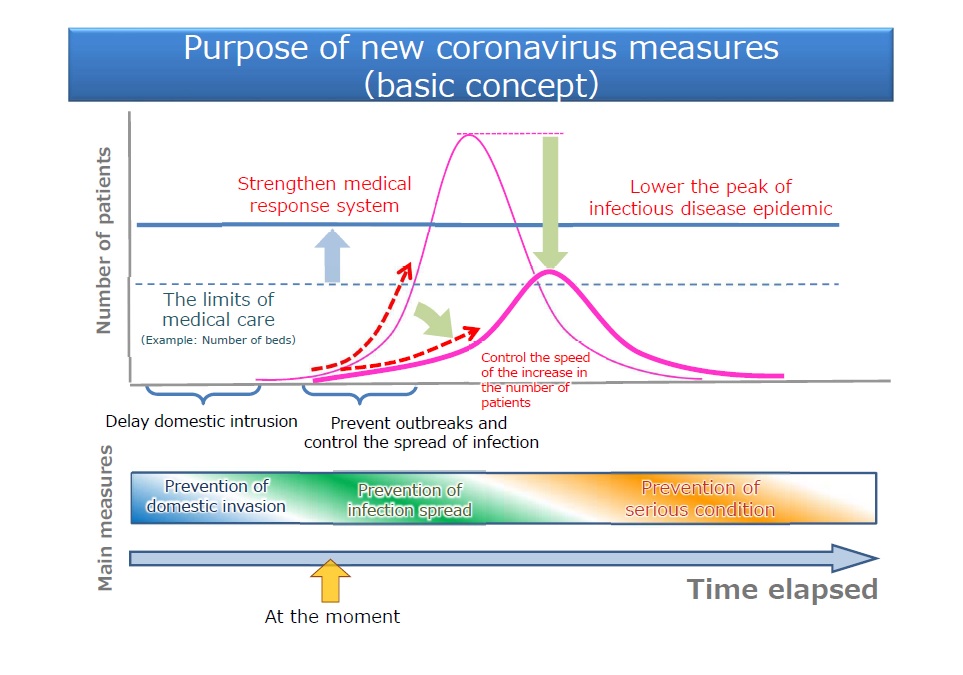
–Prevention of group infections (Counter-cluster Approach)
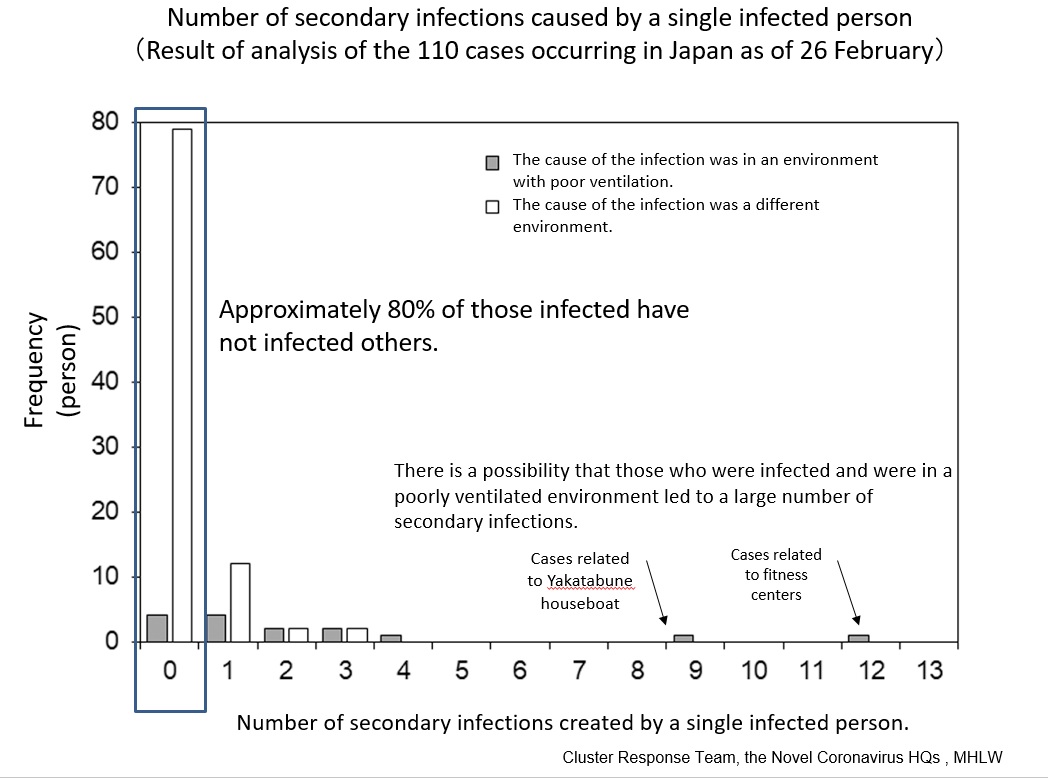
In many of the cases, the novel coronavirus does not transmit from infected persons to those around them. However, there exist several cases in which it is suspected that a single person spread the infection to many others (cases associated with Yakata-bune houseboat and fintness centers). Furthermore, there have been reported small clusters of patient outbreaks in some areas.
According to the analysis of the number of secondary transmission caused by a single infected persons, based on the relevant cases, it has been revealed that the number of secondary transmissions is significant in cases that the root of infections is in a closed space (with poor ventilation) (Graph below).
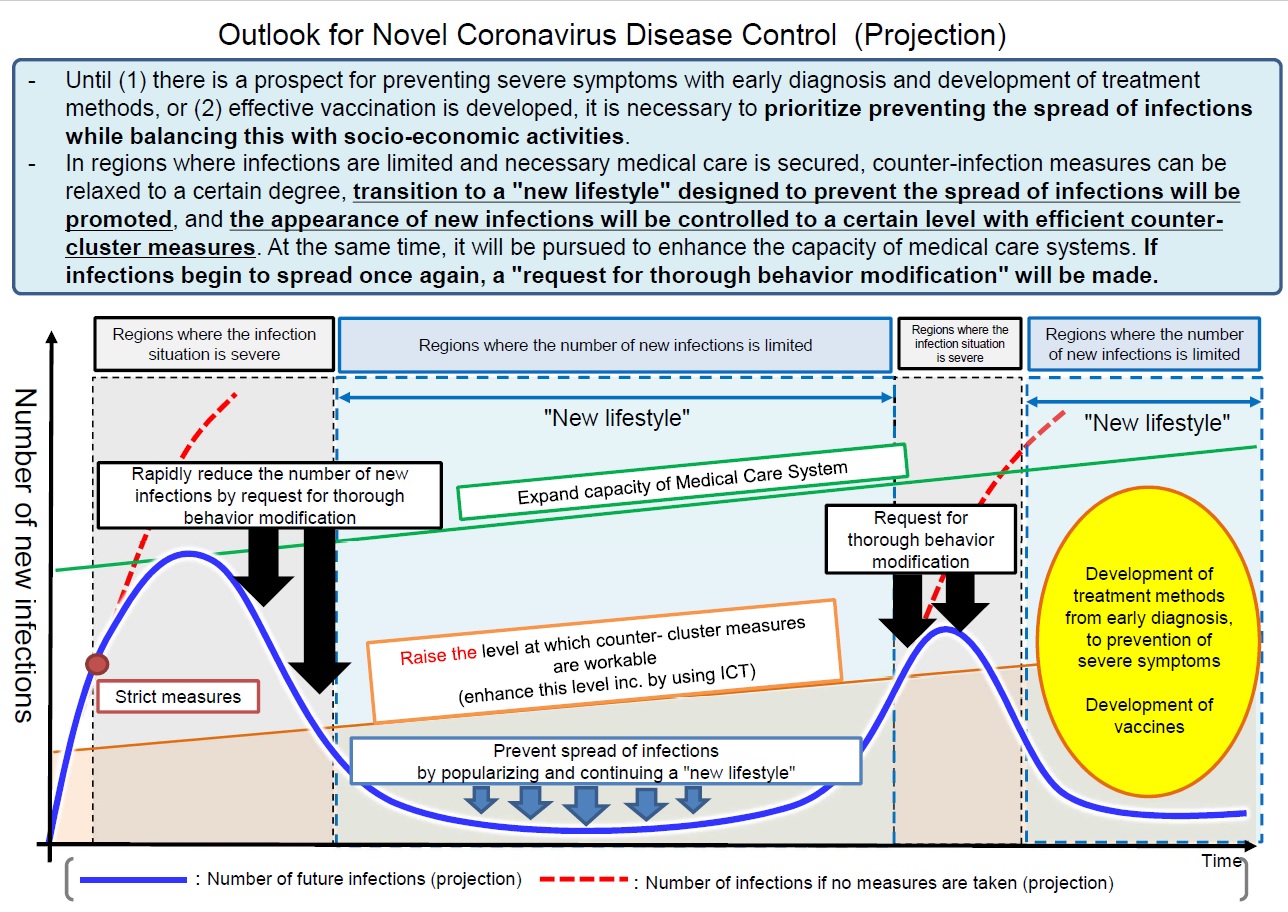
Outlook for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Projection)
- Until (1) there is a prospect for preventing severe symptoms with early diagnosis and development of treatmentmethods, or (2) effective vaccination is developed, it is necessary to prioritize preventing the spread of infectionswhile balancing this with socio-economic activities.
- In regions where infections are limited and necessary medical care is secured, counter-infection measures can berelaxed to a certain degree, transition to a "new lifestyle" designed to prevent the spread of infections will bepromoted, and the appearance of new infections will be controlled to a certain level with efficient counterclustermeasures. At the same time, it will be pursued to enhance the capacity of medical care systems. Ifinfections begin to spread once again, a "request for thorough behavior modification" will be made.
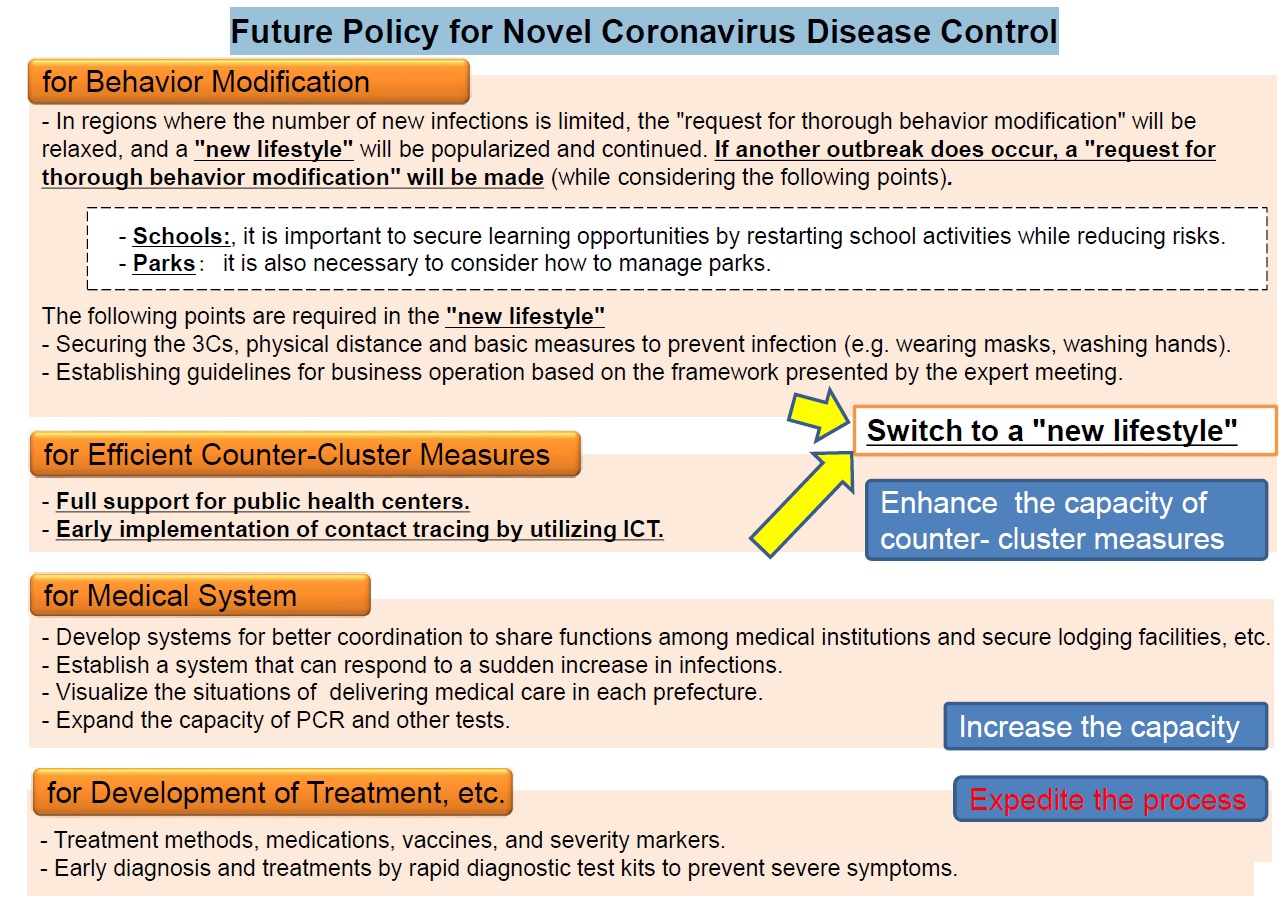
(Reference)
- Special Measures for Pandemic Influenza and New Infectious Diseases Preparedness and Response (Overview)
- Guidelines for Reimpsing the State of Emergency (Full Text)
<Overall Goal>
To maximize efforts to suppress transmission and to minimize socio-economic damage
1. Early detection of and early response to clusters
2. Enhancement of intensive care and securing medical service system for the severely ill patients, including medical equipments (Ventilator, ECMO, etc)
3. Bahavior modification of citizens
Rationale of the Government Responses
In order to end this epidemic as soon as possible, it is extremely important to prevent one cluster from developing another cluster, and the comprehensive measures must be taken. It is also significantly important to curtail the rate of increase in patients as much as possible through these preventative measures, in order to control the epidemic in Japan.
Moreover, this is also the time to establish and improve arrangements including the health system to deliver necessary medical care especially for the severe patients, to prepare for the possible increase of patients in Japan.

–Prevention of group infections (Counter-cluster Approach)
In many of the cases, the novel coronavirus does not transmit from infected persons to those around them. However, there exist several cases in which it is suspected that a single person spread the infection to many others (cases associated with Yakata-bune houseboat and fintness centers). Furthermore, there have been reported small clusters of patient outbreaks in some areas.
According to the analysis of the number of secondary transmission caused by a single infected persons, based on the relevant cases, it has been revealed that the number of secondary transmissions is significant in cases that the root of infections is in a closed space (with poor ventilation) (Graph below).

Outlook for Novel Coronavirus Disease Control (Projection)
- Until (1) there is a prospect for preventing severe symptoms with early diagnosis and development of treatmentmethods, or (2) effective vaccination is developed, it is necessary to prioritize preventing the spread of infectionswhile balancing this with socio-economic activities.
- In regions where infections are limited and necessary medical care is secured, counter-infection measures can berelaxed to a certain degree, transition to a "new lifestyle" designed to prevent the spread of infections will bepromoted, and the appearance of new infections will be controlled to a certain level with efficient counterclustermeasures. At the same time, it will be pursued to enhance the capacity of medical care systems. Ifinfections begin to spread once again, a "request for thorough behavior modification" will be made.


(Reference)
- Special Measures for Pandemic Influenza and New Infectious Diseases Preparedness and Response (Overview)
- Guidelines for Reimpsing the State of Emergency (Full Text)
Key points
1. Provision and sharing of information
Inform the public that the government will not take measures such as "lockdown" (city blockade), and call for a calm response from the people (self- restraint of travel across prefectures, such as nonessential visits to hometowns and travel, avoiding flooding of shops and panic buying).
2. Surveillance and information gathering
-Identify suspected disease carrier based on the notification from the doctor, and conduct tests that the doctor considers necessary
-Strengthen the testing system by utilizing local and private institutes. Grasp and coordinate the PCR testing system.
-Continue to develop simple test kits for rapid diagnosis.
-Strengthen the testing system by utilizing local and private institutes. Grasp and coordinate the PCR testing system.
-Continue to develop simple test kits for rapid diagnosis.
3. Pandemic Prevention
The declaration of a state of emergency on April 7 is intended to further accelerate existing measures.
On the other hand, restrictions on people's freedoms and rights must be minimal. Designated prefectures (prefectures covered by the emergency declaration) will, at first, request residents to cooperate voluntarily in self- restraint of leaving home as measures to prevent pandemic. Requests and instructions on restrictions on the use of facilities should be made after assessing the effects of such requests for voluntary cooperation in refraining from leaving home.
- Designated prefectures will take effective emergency measures taking into account the characteristics of each area and provide careful explanation to the residents. The Government Response Headquarters will coordinate with designated prefectures as necessary, listening to the opinions of experts.
- Designated prefectures will work with the government in informing the residents that the emergency measures are different from "lockdown" (city blockade). Designated prefectures will also ask people to refrain from travel across prefectures, and call for a calm response in order to prevent confusion including panic buying of food, medicine and daily necessities.
- Designated prefectures will at first request a self-restraint of going out while indicating the period and area as necessary. Examples of outing that are not covered by such request would include activities necessary for maintaining daily life such as visiting hospitals, purchasing food, medicine and daily necessities, going to work as necessary, exercising outdoors or taking a walk. Appropriate period for requesting self-restraint is about 30 days, taking into account the average period from the date of infection to the date of onset (average incubation period). However, decisions will be made flexibly to shorten or extend the period as appropriate.
- While going to work is excluded from the requests for self-restraint, designated prefectures should strongly promote teleworking. Even in case of going to work, efforts to reduce contact with people, such as staggered work hours and bicycle commuting will be promoted even more strongly than ever. In the workplace, taking thorough measures to prevent infection will be encouraged. People will be encouraged to refrain from visiting eateries with hospitality services in downtown areas, regardless of age, etc. Going out of one’s living area is also covered by the request for self- restraint.
- Businesses that perform operations essential for ensuring the stability of people's lives and the national economy (exemplified in the attachment), are required to continue their operation, depending on the characteristics of the business, while fully taking measures to prevent the spread of infection. The Government and designated prefectures will work to establish a help desk for business operators, secure logistics systems, and ensure a robust lifeline system, etc., in order to support smooth activities of these businesses.
- Designated prefectures will make request to restrict the holding of events that may lead to the spread of infection. When a request is not met with no justifiable reason, instructions will be issued and these requests and instructions will be made public.
- The Government and local governments will encourage restaurants to take necessary infection control measures to prevent places where the "3Cs" (closed spaces, crowded places, and close- contact settings) overlap. They will also ensure that request for self- restraint in going out to entertainment facilities such as cabarets and nightclubs is widely known, based on the current circumstance where clusters emerge in such place.
Prefectures in metropolitan areas will take sufficient measures described above to prevent the spread so that they will not trigger nationwide and rapid spread, in view of the high population density and their being important transportation hubs.
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology will disseminate the guiding principle on temporary closure of schools. Prefectural governments will provide guidance to school operators on infectious disease countermeasures such as health management. The Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare will provide guiding principles of nursery schools and after-school children's clubs, etc. regarding the down-sizing of childcare and temporary closure of facilities. In this regard, the Ministry will also present guidance on securing childcare during such temporary closure for children of medical staff, those who need to continue working to maintain social functions, and those who have difficulty taking off work including single-parents.
On the other hand, restrictions on people's freedoms and rights must be minimal. Designated prefectures (prefectures covered by the emergency declaration) will, at first, request residents to cooperate voluntarily in self- restraint of leaving home as measures to prevent pandemic. Requests and instructions on restrictions on the use of facilities should be made after assessing the effects of such requests for voluntary cooperation in refraining from leaving home.
- Designated prefectures will take effective emergency measures taking into account the characteristics of each area and provide careful explanation to the residents. The Government Response Headquarters will coordinate with designated prefectures as necessary, listening to the opinions of experts.
- Designated prefectures will work with the government in informing the residents that the emergency measures are different from "lockdown" (city blockade). Designated prefectures will also ask people to refrain from travel across prefectures, and call for a calm response in order to prevent confusion including panic buying of food, medicine and daily necessities.
- Designated prefectures will at first request a self-restraint of going out while indicating the period and area as necessary. Examples of outing that are not covered by such request would include activities necessary for maintaining daily life such as visiting hospitals, purchasing food, medicine and daily necessities, going to work as necessary, exercising outdoors or taking a walk. Appropriate period for requesting self-restraint is about 30 days, taking into account the average period from the date of infection to the date of onset (average incubation period). However, decisions will be made flexibly to shorten or extend the period as appropriate.
- While going to work is excluded from the requests for self-restraint, designated prefectures should strongly promote teleworking. Even in case of going to work, efforts to reduce contact with people, such as staggered work hours and bicycle commuting will be promoted even more strongly than ever. In the workplace, taking thorough measures to prevent infection will be encouraged. People will be encouraged to refrain from visiting eateries with hospitality services in downtown areas, regardless of age, etc. Going out of one’s living area is also covered by the request for self- restraint.
- Businesses that perform operations essential for ensuring the stability of people's lives and the national economy (exemplified in the attachment), are required to continue their operation, depending on the characteristics of the business, while fully taking measures to prevent the spread of infection. The Government and designated prefectures will work to establish a help desk for business operators, secure logistics systems, and ensure a robust lifeline system, etc., in order to support smooth activities of these businesses.
- Designated prefectures will make request to restrict the holding of events that may lead to the spread of infection. When a request is not met with no justifiable reason, instructions will be issued and these requests and instructions will be made public.
- The Government and local governments will encourage restaurants to take necessary infection control measures to prevent places where the "3Cs" (closed spaces, crowded places, and close- contact settings) overlap. They will also ensure that request for self- restraint in going out to entertainment facilities such as cabarets and nightclubs is widely known, based on the current circumstance where clusters emerge in such place.
Prefectures in metropolitan areas will take sufficient measures described above to prevent the spread so that they will not trigger nationwide and rapid spread, in view of the high population density and their being important transportation hubs.
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology will disseminate the guiding principle on temporary closure of schools. Prefectural governments will provide guidance to school operators on infectious disease countermeasures such as health management. The Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare will provide guiding principles of nursery schools and after-school children's clubs, etc. regarding the down-sizing of childcare and temporary closure of facilities. In this regard, the Ministry will also present guidance on securing childcare during such temporary closure for children of medical staff, those who need to continue working to maintain social functions, and those who have difficulty taking off work including single-parents.
4. Medical cares, etc.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare will notify and ensure the following measures, from the viewpoint of thoroughly preventing nosocomial infection in medical institutions and facilities for the elderly, under cooperation with local governments.
- Take every possible precaution to prevent workers from being a source of infection by thoroughly avoiding the place where "3Cs" overlap at the same time, by making sure for workers to wear masks, wash and disinfect hands, disinfect regularly shared facilities, maintain a certain distance each other when eating and drinking, keep their daily health tracks and stay home if their physical condition is not perfect.
- Temporarily cease reception of visits except for emergency in order to prevent infection from visiting persons.
- Consider measures such as suspending or restricting temporary use of facilities such as day-care, limiting outings and overnight stays of inpatients and users, in areas where infection is prevalent.
- Isolate a suspected case immediately and implement infection countermeasures under the guidance of public health centers, in case of suspecting a new case of COVID-19 infection from hospitalized patients or users,
The Government and prefectures will prioritize securing personal protective equipment such as masks for medical institutions that conduct PCR tests and admit patients for hospitalizations, and will take the initiative to ensure PCR tests conducted for medical personnel, workers and inpatients.
- Take every possible precaution to prevent workers from being a source of infection by thoroughly avoiding the place where "3Cs" overlap at the same time, by making sure for workers to wear masks, wash and disinfect hands, disinfect regularly shared facilities, maintain a certain distance each other when eating and drinking, keep their daily health tracks and stay home if their physical condition is not perfect.
- Temporarily cease reception of visits except for emergency in order to prevent infection from visiting persons.
- Consider measures such as suspending or restricting temporary use of facilities such as day-care, limiting outings and overnight stays of inpatients and users, in areas where infection is prevalent.
- Isolate a suspected case immediately and implement infection countermeasures under the guidance of public health centers, in case of suspecting a new case of COVID-19 infection from hospitalized patients or users,
The Government and prefectures will prioritize securing personal protective equipment such as masks for medical institutions that conduct PCR tests and admit patients for hospitalizations, and will take the initiative to ensure PCR tests conducted for medical personnel, workers and inpatients.
5. Economic and employment measures
Expeditiously implement necessary and sufficient economic and fiscal policies without pause, taking bold measures to return the Japanese economy to a solid growth trajectory.
6. Other important considerations
Consideration for human rights including prevention of reputational damage of medical personnel, etc.
Request, based on the Act, of emergency transportation and procurement of goods and materials necessary to secure the operation of the medical system, etc.
Maintaining social functions;
- Measures to prevent infection of personnel of government organizations and other public institutions and to ensure continuance of their duties
- Continued operation of businesses essential to ensuring the stability of people's lives and the national economy
Request, based on the Act, of emergency transportation and procurement of goods and materials necessary to secure the operation of the medical system, etc.
Maintaining social functions;
- Measures to prevent infection of personnel of government organizations and other public institutions and to ensure continuance of their duties
- Continued operation of businesses essential to ensuring the stability of people's lives and the national economy