(1) Government Procurement Seminar
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs holds a seminar on government procurement each year, based on the Action Program on Government Procurement adopted at the 20th Meeting of the Action Program Committee in February 1994 and on the Procedures for Government Procurement on Products (Operational Guidelines) adopted at the 21st Meeting of the Action Program Committee held in March 1994. In 2000, the seminar was held from 25 to 26 April (with 78 domestic and 35 foreign suppliers participating).
The above two voluntary measures also call for the other ministries and agencies to hold seminars on government procurement as necessary. In 1999, the following seminars were held.
Table III-1 Government Procurement Seminars in Japanese Ministries and Agencies in 2000
| Procurement Organization | Date | Content |
| National Public Safety Commission (National Police Agency) | 26 May 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Telecommunications) |
| Defense Agency | 2 June 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Medical Technology) |
| Ministry of Education | 10 May 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Telecommunications, Medical Technology) |
| Ministry of Health and Welfare | 15 May 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Medical Technology) |
| Ministry of International Trade and Industry | 30 May 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Medical Technology) |
| Ministry of Transport | 28 April 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Telecommunications, Medical Technology) |
| Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications | 28 April 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Telecommunications, Medical Technology) |
| Ministry of Construction | 28 April 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Telecommunications) |
| Labour Welfare Corp. | 29 May 2000 | Government Procurement Seminar, Government Procurement Annual Meeting (Medical Technology) |
(2) Voluntary Review Meeting
In 1999, by means of hearings and questionnaires conducted on 5 November, the opinions of domestic and overseas suppliers were solicited concerning implementation and utilization of voluntary measures. In addition, another voluntary review, a follow-up to the voluntary measures based on statistics, etc., was held on 3 December and gave consideration to the results of the hearings (Reference Materials III-4). The Voluntary Review Meeting drew up the Government Initiative on Future Management of Government Procurement (Reference Materials III-5) based upon the reviews above.
(3) Action Program Committee
On 25 April 2000, the 31st Action Program Committee approved partial revisions to the "Procedures to Introduce Supercomputers." Concerning procurement contracts concluded after 1st May 2000, the committee agreed to raise the theoretical peak ratings threshold that stipulates the coverage of the "Introduction Procedures." In addition, in the Action Program Committee held on 30 November, the state of the implementation of the voluntary measures reviewed at the voluntary review meeting was confirmed, and the Government Initiative on Future Management of Government Procurement drawn by the voluntary review committee was approved.
(4) Thresholds
Thresholds, which vary according to types of contract specified in the WTO Agreement on Government Procurement, are obtained by converting the applied standard values (in SDR) into the national currency (The Standard Values are revised every two fiscal years.).
The thresholds in the voluntary measures related to government procurement as formulated by the Action Program Committee are revised according to these notifications. The thresholds applicable at present may be found in Reference Material III-6.
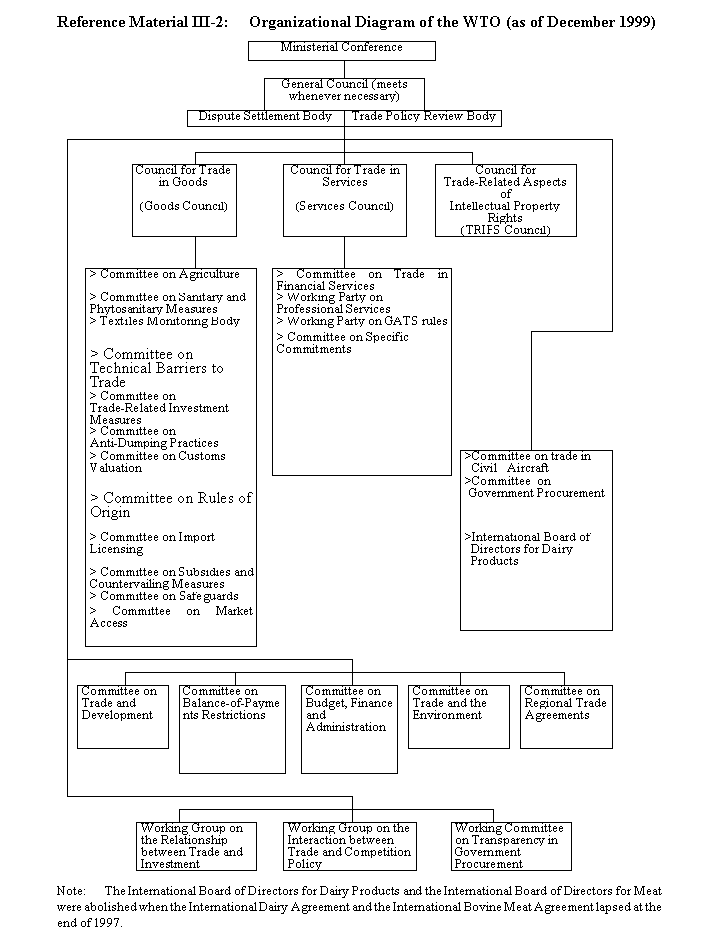
Reference Material III-1:
World Trade Organization Agreement on Government Procurement
| The Marrakesh Agreement Establishing the World Trade Organization (WTO Founding Agreement) |
| Attached Document I |
| Attached Document IA: Multilateral Agreements on Trade in Goods |
| (1) | General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 1994 (GATT 1994) |
| (2) | Agreement on Agriculture |
| (3) | Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures |
| (4) | Agreement on Textiles and Clothing (ATC) |
| (5) | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (Standard Agreement) |
| (6) | Agreement on Trade-Related Investment Measures |
| (7) | Agreement on Implementation of Article VI of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 1994 (Anti-Dumping Agreement) |
| (8) | Agreement on Implementation of Article VII of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 1994 (Customs Valuation Agreement) |
| (9) | Agreement on Preshipment Inspection |
| (10) | Agreement on Rules of Origin |
| (11) | Agreement on Import Licensing Procedures |
| (12) | Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures |
| (13) | Agreement on Safeguards |
| Attached Document IB: General Agreement on Trade in Services |
| Attached Document IC: Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights |
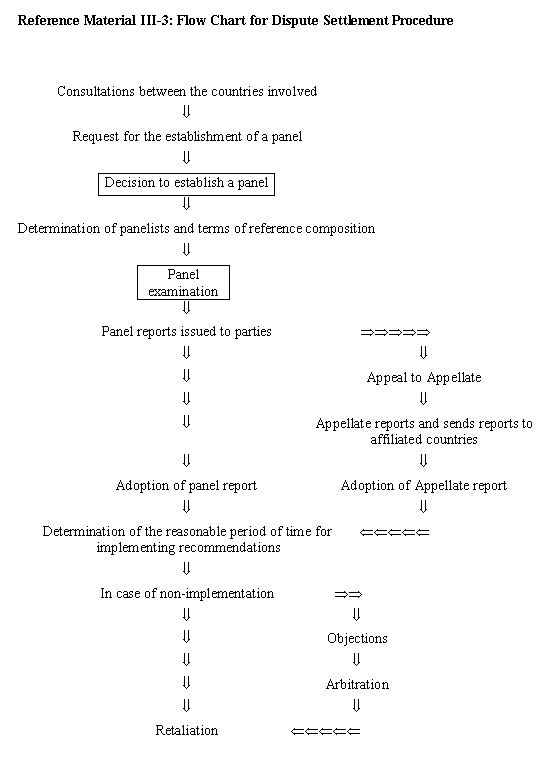
| Attached Document II: Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes |
| Attached Document III: Trade Policy Review Mechanism |
| Attached Document IV: Plurilateral Trade Agreements |
| (1) | Agreement on Trade in Civil Aircraft |
| (2) | Agreement on Government Procurement |
| (3) | International Dairy Agreement (lapsed at the end of 1997) |
| (4) | International Bovine Meat Agreement (lapsed at the end of 1997) |
Reference Material III-4: Results of the Inquiries to Domestic and Foreign Suppliers (2000)
| Questionnaire Items | Ratio (%) |
| In all fields | |
| Utilization of the information on government procurements offered at the beginning of each fiscal year: | |
| a) Actively utilizing it. | 61.4 |
| b) Sometimes utilizing it. | 29.5 |
| c) Not making use of it. | 9.1 |
| Usefulness of individual pieces of information on government procurements | |
| a) Very satisfied. | 26.2 |
| b) Generally satisfied. | 71.4 |
| c) Dissatisfied. | 2.4 |
| Annual Report ("Japan's Government Procurement: Policy and Achievements") | |
| a) Satisfied with the contents and make use of it. | 18.2 |
| b) Generally satisfied. | 43.2 |
| c) Not making use of it. | 38.6 |
| Securing competitiveness through the reduction of single tendering and selective tendering among designated bidders | |
| a) Sufficiently secured. | 50.0 |
| b) Somewhat secured, but not sufficiently. | 43.2 |
| c) Not secured. | 6.8 |
| Implementation status of the overall-greatest-value evaluation method | |
| a) Sufficiently contributes to reasonable evaluation and secures competitiveness. | 43.9 |
| b) Somewhat contributes to reasonable evaluation and secures competitiveness | 46.3 |
| c) Does not contribute very much to reasonable evaluation or secure competitiveness. | 9.8 |
| Complaint review system | |
| a) Considered utilizing the complaint review system. | 0.0 |
| b) Never considered utilizing the complaint review system. | 68.2 |
| c) Have insufficient information about the complaint review system. | 31.8 |
| Questionnaire Items | Ratio (%) |
| All telecommunications and medical technology fields | |
| Fairness of technical specifications | |
| a) Specified in accordance with the measures. | 13.8 |
| b) Specified largely in accordance with the measures | 79.3 |
| b) Specified not in accordance with the measures | 6.9 |
| Evaluation method in the Standard Guide to the Overall-greatest-value methodology | |
| a) Considered utilizing the complaint review system. | 21.4 |
| b) Never considered utilizing the complaint review system. | 75.0 |
| c) Have insufficient information about the complaint review system. | 3.6 |
| Threshold for overall-greatest value evaluation method (385,000 SDRs) | |
| a) Appropriate. | 79.3 |
| b) Needs to be reduced. | 13.8 |
| c) Needs to be raised. | 6.9 |
* Fifty-five respondents took part in the questionnaire (25 from products in general, 9 from the area of telecommunications products, and 20 from the area of medical technology), excluding those who did not respond.
* Due to rounding of figures, the totals do not add up to 100% in some cases.
The Voluntary Review Meeting has confirmed the following points, based on the results of interviews with suppliers regarding the implementation of various voluntary measures to facilitate market access and ensure openness, fairness and competitiveness in the field of government procurements of goods and services.
| 1. | Efforts will be made to more strictly apply of the conditions in the Article 15 of the WTO Agreement, with reference to the discussions of the Voluntary Review Meeting in March 2000. Special attention will continue to be paid to implementing the appropriate internal examinations for new single tendering contracts. For continuing matters as well, attention will be paid so that there is no easy application of reasoning such as compatibility. |
| 2. | With regard to the application of the Overall Greatest Value (OGV) Evaluation
Method, further effort will be made, within the scope of the Standard Guides,
to utilize the method effectively, by providing appropriate evaluation criteria
for factors other than price and weighting them properly. In addition, efforts will be made to make it possible to perform the administrative costs more efficiently, for both the procuring side as well as the suppliers, by keeping the requested materials for OGV evaluation to the minimum requirement. |
| 3. | For additional procurement with the estimated value of 100,000 SDR or more, such as procurements associated with supplementary budgets, efforts will be made to publicize their information as soon as possible. |
| 4. | Continuous efforts will also be made to implement the publication of information on awarding of contracts in the official gazette ("Kanpo") as quickly as possible. |
The standard values for all types of voluntary measures determined in the Committee for Drawing Up and Promoting the Action Program, based on Notification No. 14 of the Ministry of Finance as published in the official gazette (Kanpo) dated 25 January 2000, have been set as follows: (Applying to procurement contracts awarded between 1 April 2000 and 31 March 2002)
| SDR 500 | equivalent to 81,000 yen | |
| SDR 100,000 | equivalent to 17 million yen | |
| SDR 385,000 | equivalent to 63 million yen | |
| SDR 800,000 | equivalent to 130 million yen | |
| SDR 2 million | equivalent to 330 million yen | |
| SDR 5 million | equivalent to 810 million yen |
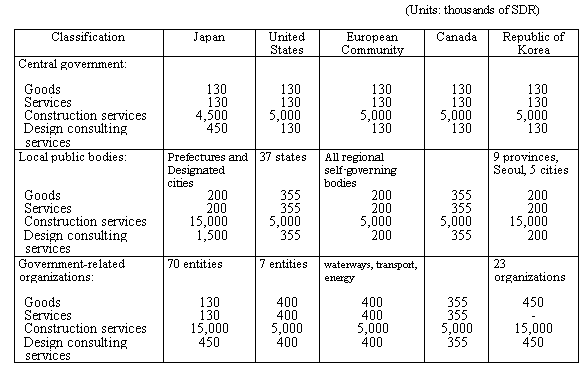
1. Overview of Standard Values for Japan
(1) Standard Values for the WTO Agreement on Government Procurement
| Classification | Central government | Local public bodies | Government-related organizations |
| Products | 21 million yen (SDR 130,000) |
33 million yen (SDR 200,000) |
21 million yen (SDR 130,000) |
| Services | 21 million yen (SDR 130,000) |
33 million yen (SDR 200,000) |
21 million yen (SDR 130,000) |
| Construction services | 750 million yen (SDR 4.5 million) |
2.5 billion yen (SDR 15 million) |
2.5 billion yen (SDR 15 million) |
| Design consulting services |
72 million yen (SDR 450,000) |
250 million yen (SDR 1.5 million) |
75 million yen (SDR 450,000) |
(Note) The above values converted to Japanese currency are applicable between 1 April 2000 and 31 March 2002.
(2) Standard Values for Voluntary Measures
The voluntary measures on government procurement determined by the Committee for
Drawing Up and Promoting the Action Program have been modified so that the standard
values for products and services for the central government and government-related
organizations have been lowered from SDR 130,000 (21 million yen) to SDR 100,000
(17 million yen).
2. International comparison of standard values