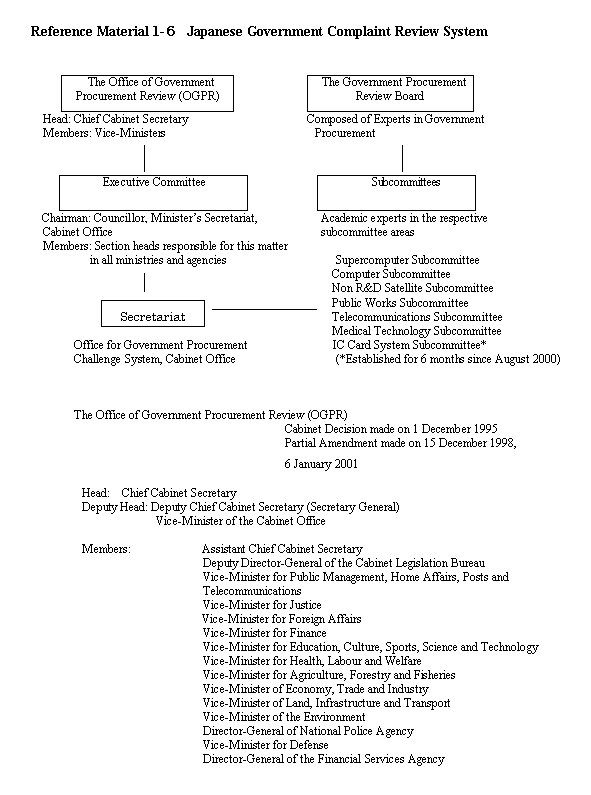
a. The system under the former Agreement on Government Procurement
Various regulations were stipulated under non-discrimination and national treatment policies, etc., in the GATT Agreement on Government Procurement which came into effect in 1981. However no regulations were stipulated in regard to complaint review procedures.
On the other hand, regulations relating to a system of complaint review procedures have been established in each voluntary measure adopted by the Action Program Committee, and a complaint review procedure is implemented based on these regulations.
b. The system under the new WTO Agreement on Government Procurement (reference material I - 5)
The WTO Agreement on Government Procurement came into effect in 1996 at the Uruguay Round of GATT. In addition to the regulations regarding non-discrimination and national treatment policies found in the former Agreement, in regard to complaint review, Article 20: Challenge Procedures, was established.
It thus became necessary for the Government of Japan to develop a system, incorporating the system for complaint review procedures which had been in place until that point, in order to carry out its duties according to the new Agreement, in the period before the new Agreement on Government Procurement came into effect. For this purpose, the Office of Government Procurement Review was established following a Cabinet decision, "The Establishment of Headquarters of Government Procurement Review" on 1 December 1995. It was determined that the Headquarters would set up a Government Procurement Review Board to handle complaints, and the responsibility for the complaint review procedure based on the voluntary measures decided by the Action Program Committee was transferred to a new organization.
In conjunction with the reorganization of the central ministries on January 6, 2001, this office is established in the Cabinet Office.
c. Results on complaints in 2001
Case No.3
1. Date of filing of the complaint: February 17, 2001
2. Name of complainant: Jobi Co..
3. Name of procuring entity concerning the complaint: Yamaguchi University
4. Name of procured goods/services concerning the complaint: Building-cleaning services
5. Outline of complaint:
The contract of supply services of personnel concerning the cleaning of a part of the university buildings, between the procuring entity concerned and the supplier is not performed based on the Agreement on Government Procurement; GPA.
6. Outline of the status of complaint review
The procurement contract concerned was not on building-cleaning services (CPC874) but on placement and supply services on personnel (CPC872) that was not covered by the Annex 4 of Japan's Appendix I in the GPA. For that reason, the Board decided not to accept the complaint on February 26, 2001, and informed the complainant and the procuring entity.
Case No.4
1. Date of filing of the complaint: October 9, 2001
2. Name of complainant: IBM Japan Ltd.
3. Name of the procuring entity concerning the complaint: Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute
4. Name of procured goods/services concerning the complaint: ITBL calculation system
5. Outline of complaint:
As undermentioned, the procuring entity disqualified the complainant, violating "the Agreement on Government Procurement" and "Procedures to Introduce Supercomputers"(the decision of the Committee for Drawing Up and Promoting the Action Program on July 16, 1987). The entity's violation of the rule is so serious that the complainant claimed reexamination of its tender.
(1) The complainant's proposal for revision of specifications was rejected as an overdue comment even though 50-day-proposal term was regulated.
(2) A function that was not referred in the final specifications was considered in the qualification procedures.
6. Outline of the status of complaint review
The Government Procurement Review Board released a report on the case, and sent it to the entity and the complainant. In the report, the Board judged that the procurement entity concerned committed a violation of procurement procedure. However, since the system proposed by the complainant does not meet the requirement in the specifications prepared by the procurement entity, the Board cannot but approve in the end the result of the procurement procedures and reject the complainant's petition demanding correction measures from the procurement entity concerned.
(2) Construction sector
While the bidding and contracting procedures for public works are not covered by the Action Program Committee, the "Major Projects Arrangements" and the "Additional Measures of the Government of Japan on Major Projects Arrangements" were adopted by the Cabinet, in May 1987 and in July 1991, respectively, both of which were intended to increase access to large scale public works projects. Furthermore, in January 1994, the "Action Plan on Reform of the Bidding and Contracting Procedures for Public Works," which included adoption of open and competitive tendering procedures for procurement with a value above a certain threshold, was adopted by the Cabinet. In order to improve the actual operation of the Action Plan, Operational Guidelines with Respect to the Action Plan on Reform of the Bidding and Contracting Procedures for Public Works were drafted in June 1996. (Administrative Vice Ministers' Conference).
In November 2000, in the context of these measures, "Act for Promoting Tendering and Contracting for Public Works" was enacted to promote transparency and fair competition in tendering and contracting procedures for public works. The law entered into force in April 2001.
Reference Material�T-5
Entities Covered by the Voluntary Measures on Government Procurement
| Entities Covered by the Voluntary Measures (154) | ||
| A. Entities Covered by the Agreement on Government Procurement (147) | ||
| Central Government Entities (21) | Public Corporations (69) | Independent Administrative Institutions (57) |
| House of Representatives; House of Councilors; Supreme Court; Board of Audit, Cabinet; National Personnel Authority; Cabinet Office; Imperial Household Agency; National Public Safety Commission; Defense Agency; Financial Services Agency; Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications; Ministry of Justice; Ministry of Foreign Affairs; Ministry of Finance; Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology; Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare; Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries; Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport; Ministry of the Environment | Water Resources Development Public; Japan Regional Development Corporation; Japan Green Resources Corporation; Japan National Oil Corporation; Japan Railway Construction Public Corporation; New Tokyo International Airport Authority; Japan Highway Public Corporation; Metropolitan Expressway Public Corporation; Hanshin Expressway Public Corporation; Honshu-Shikoku Bridge Authority; Urban Development Corporation; Japan Science and Technology Corporation; Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute; Japan Environment Corporation; Japan International Cooperation Agency; Social Welfare and Medical Service Corporation; Government Pension Investment Fund; Agriculture and Livestock Industries Corporation; Metal Mining Agency of Japan; Japan Small and Medium Enterprise Corporation; Postal Life Insurance Welfare Corporation; Labor Welfare Corporation; Employment and Human Resources Development; Okinawa Development Finance Corporation; National Life Finance Corporation; Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Finance Corporations; Japan Finance Corporation for Small Business; Housing Loan Corporation; Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises; Development Bank of Japan; Japan Bank for International Cooperation; Teito Rapid Transit Authority; Japan Tobacco Inc.; Hokkaido Railway Company; East Japan Railway Company; Central Japan Railway Company; West Japan Railway Company; Shikoku Railway Company; Kyusyu Railway Company; Japan Freight Railway Company; Nippon Telegraph and Telephone CO.; Northern Territory Issue Association; Japan Consumer Information Center; Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute; RIKEN(The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research); The Pollution-related Health Damage Compensation and Prevention Association; Fund for the Promotion and Development of the Amami Islands; Japan Foundation; Japan Scholarship Foundation; Japan Arts Council; Japan Society for the Promotion of Science; University of the Air Foundation; National Stadium and School Health Center of Japan; Social Insurance Medical Fee Payment Fund; Association for Welfare of the Mentally and Physically Handicapped; Japan Racing Association; Mutual Aid Association of Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Corporation Personnel; National Association of Racing; Farmers'Pension Fund; Japan Keirin Association; Japan External Trade Organization; Japan Motorcycle Racing Organization; New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization; Japan National Tourist Organization; Japan Institute Labor; Mutual Aid Fund for Official Casualties and Retirement of Volunteer Firemen; Corporation for Advanced Transport & Technology; Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private School; Organization for Workers Retirement Allowance Mutual Aid; | National Archives of Japan; Communication Research Laboratory; Institute of Fire and Disaster National Research; National Research Institute of Brewing; National Center for University Entrance Examination; National Institute of Special Education; National Olympic Memorial Youth Center; National Women's Education Center; National Youth Houses; National Children's Center; National Institute for Japanese Language; National Science Museum; National Institute for Materials Science; National Research Institute for Earth Sciences and Disaster Prevention; National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan; National Institute of Radiological Sciences; National Museum of Art; National Museum; National Research Institute for Cultural Properties; National Center for Teacher's Development; The National Institute of Health and Nutrition; National Institute of Industrial Safety; National Institute of Industrial Health; Center for Food Quality, Labeling and Consumer services; National Center for Seeds and Seedlings; National Livestock Breeding Center; Fertilizer and Feed Inspection Station; Agricultural Chemicals Inspection Station; National Farmers Academy; Forest Tree Breeding Center; National Salmon Resources Center; National Fisheries University; National Agricultural Research Organization; National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences; National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences; National Institute for Rural Engineering; Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences (JIRCAS); Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute; Fisheries Research Agency; Research Institute of Economy, Trade and Industry; National Center for Industrial Property Information; Nippon Export and Investment Insurance; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology; National Institute of Technology and Evaluation; Public Works Research Institute; Building Research Institute; National Traffic Safety and Environment Laboratory; National Maritime Research Institute; Port and Airport Research Institute; Electronic Navigation Research Institute; Civil Engineering Research Institute of Hokkaido; Marine Technical College; National Institute for Sea Training; School for Seafarers Training; Civil Aviation College; The National Institute for Environmental Studies; |
| B. Entities only covered by the "Computer Measures" (7) | ||
| National Space Development Agency of Japan; The Shoko Chukin Bank; Electric Power Development Co., Ltd.; Kansai International Airport CO., Ltd; The Japan Shipbuilding Industry; Foundation; Japan Broadcasting Corporation; Japan Worker's Housing Association; | ||
